Python is a type of computer language that people use to tell computers what to do. It's like giving instructions to your computer so it can perform tasks. Python is known for being easy to understand and write, making it popular for beginners and professionals alike.
Guido van Rossum, a Dutch programmer, created Python. He started working on Python in the late 1980s and officially released it in 1991. Guido van Rossum aimed to make a programming language that was easy to read and write, like plain English.
Python consists of different elements that help in writing instructions for computers. These include:
Syntax: Rules and structure for writing Python code.
Functions: Pre-written pieces of code that perform specific tasks.
Libraries: Collections of functions and tools for specific purposes, like web development, data analysis, or artificial intelligence.
Variables: Names used to store data that can be used and changed in the code.
Loops and Conditions: Control structures that let you repeat tasks or make decisions in your code.
Overall, Python is like a toolbox full of easy-to-use tools that help you build all kinds of things with your computer, whether it's websites, games, analyzing data, or automating tasks.
How to install Python?
How to install Python in Windows?
Go to the Python website: Open your web browser and go to www.python.org.
DownloadPython: On the Python website, click on the "Downloads" tab. You'll see a button that says "Download Python." Click on it.
Choose the installer: You'll be directed to a page with different versions of Python. The latest version is usually displayed at the top. Click on the "Download" button next to the version you want. For most users, the recommended version is fine.
Run the installer: Once the download is complete, find the downloaded file (it's usually in your Downloads folder) and double-click on it to run the installer.
Start the installation: A window will pop up with options for installing Python. Make sure to check the box that says "Add Python to PATH." This option makes it easier to run Python commands from the Command Prompt. Then, click "Install Now" to start the installation process.
Wait for installation: The installer will then install Python on your computer. This may take a few minutes, so be patient.
Finish installation: Once the installation is complete, you'll see a message saying "Setup was successful." Click on the "Close" button to exit the installer.
Verify installation: To make sure Python installed correctly, open the Command Prompt by typing "cmd" in the Windows search bar and pressing Enter. Then, type "python" and press Enter. You should see a message with the Python version number, and the Python interactive shell should open.
That's it! Python is now installed on your Windows computer, and you're ready to start coding. You can close the Command Prompt for now, and whenever you want to write and run Python code, just open the Command Prompt again and start typing your commands.
How to install python in Linux?
Open Terminal: Launch the Terminal on your Linux system. You can usually find it by searching for "Terminal" in the applications menu.
Update package list: It's a good practice to update your package list before installing new software. Type the following command in the Terminal and press Enter:
sudo apt update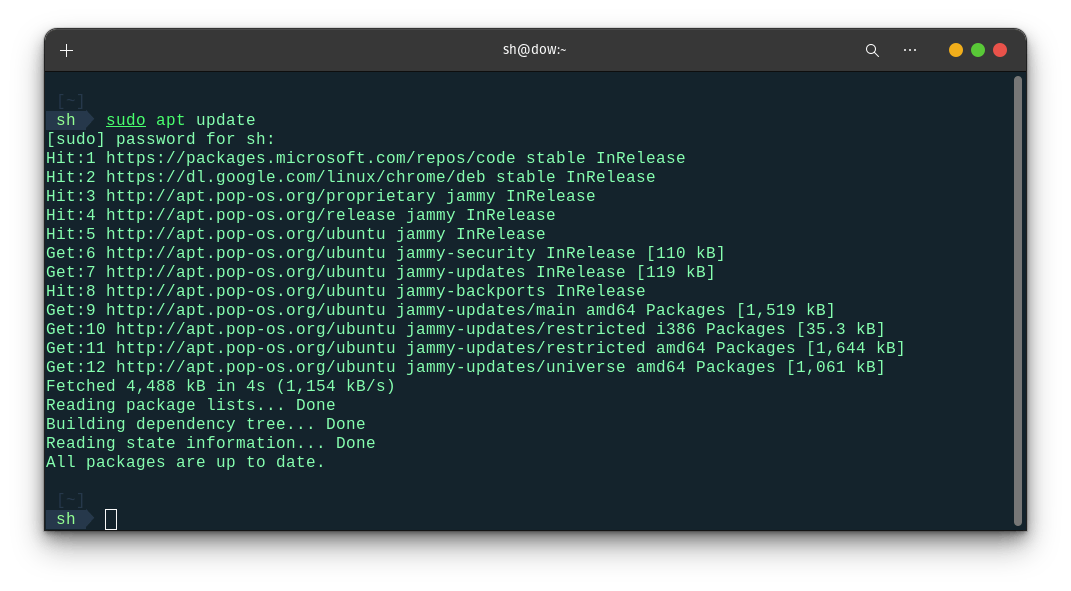
Install Python: Most Linux distributions come with Python pre-installed, but if it's not, you can install it easily using the package manager. In the Terminal, type the following command and press Enter:
sudo apt install python3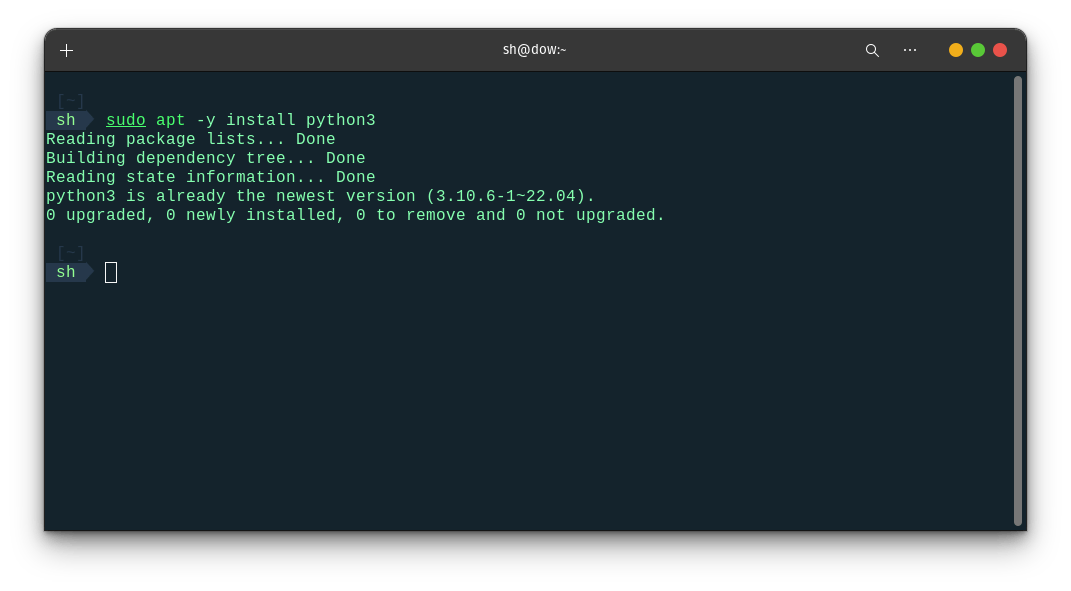
This command will install Python 3, which is the latest version. If you specifically need Python 2, you can replace "python3" with "python" in the command.
Verify installation: Once the installation is complete, you can verify that Python is installed correctly by typing the following command in the Terminal and pressing Enter:
python3 --version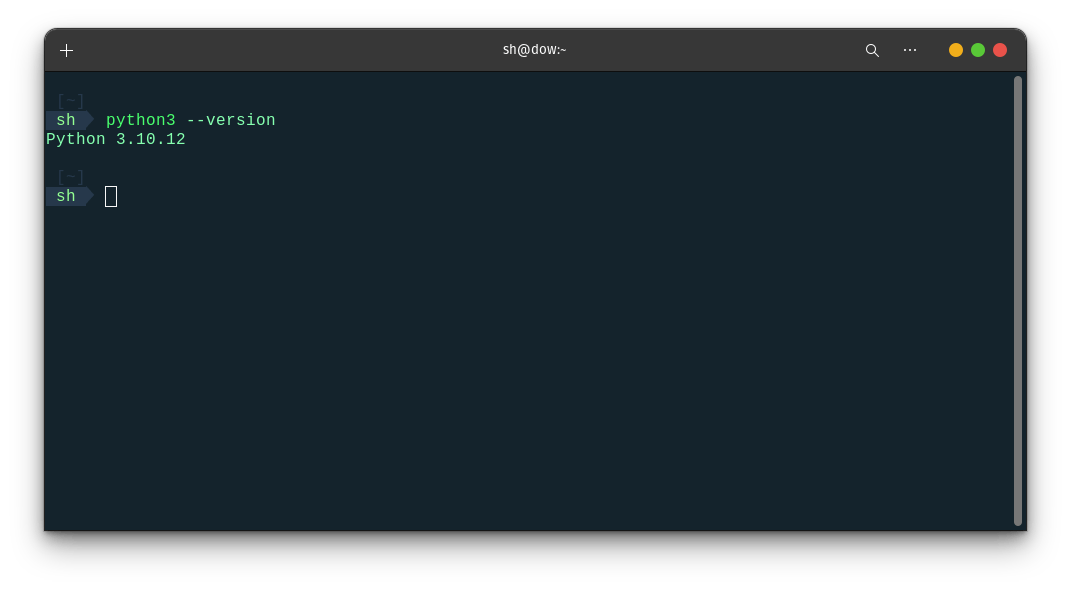
This command will display the version number of Python installed on your system.
Optional: Install pip: Pip is a package manager for Python that allows you to easily install and manage Python libraries and dependencies. To install pip, type the following command in the Terminal and press Enter:
sudo apt install python3-pip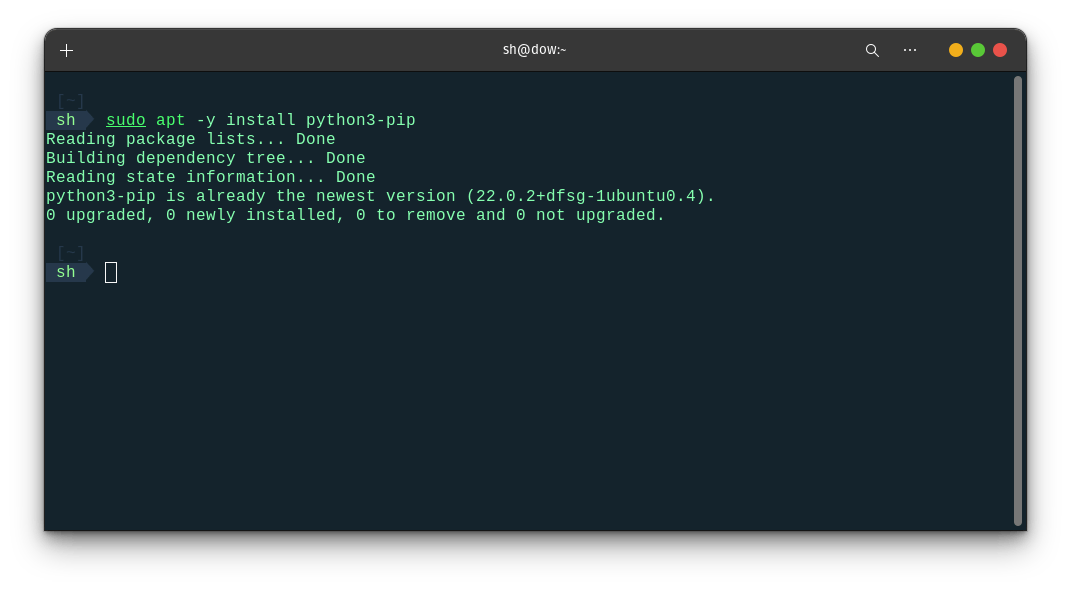
Verify pip installation (optional): You can verify that pip is installed correctly by typing the following command in the Terminal and pressing Enter:
pip3 --version
This command will display the version number of pip installed on your system.
That's it! Python is now installed on your Linux system, and you're ready to start coding. You can close the Terminal, and whenever you want to write and run Python code, just open the Terminal again and start typing your commands.
Data Types in Python
Integer (int): Integers are whole numbers without any decimal point. For example, 5, -10, and 1000 are integers.
Float (float): Floats are numbers with decimal points. For example, 3.14, -0.5, and 2.71828 are floats.
String (str): Strings are sequences of characters, enclosed within single (' ') or double (" ") quotes. For example, "Hello, world!", 'Python', and "123" are strings.
Boolean (bool): Booleans represent truth values, either True or False. Booleans are often used for conditions and comparisons in programming.
List: Lists are ordered collections of items, separated by commas and enclosed within square brackets ([]). Lists can contain elements of different data types. For example, [1, 2, 3], ['apple', 'banana', 'orange'], and [1, 'hello', True] are lists.
Tuple: Tuples are similar to lists but are immutable, meaning they cannot be changed after creation. Tuples are enclosed within parentheses (()). Example: (1, 2, 3), ('a', 'b', 'c'), and (True, False, True) are tuples.
Dictionary (dict): Dictionaries are collections of key-value pairs, enclosed within curly braces ({}). Each key is associated with a value. Keys are unique within a dictionary, but values can be duplicated. Example: {'name': 'John', 'age': 30, 'city': 'New York'} is a dictionary.
Set: Sets are unordered collections of unique elements, enclosed within curly braces ({}). Sets do not allow duplicate values. Example: {1, 2, 3}, {'apple', 'banana', 'orange'}, and {True, False} are sets.
These are some of the basic data types in Python. Understanding them is essential for working with data and writing effective Python code
"Fuel my passion and support my journey by clicking 'Buy me a coffee' today!"
~Dipen : )

